ESG Reporting
What is ESG Reporting?
ESG reporting involves the disclosure of data covering a company’s operations in three areas: Environmental, Social, and Governance. It’s a way for companies to showcase their efforts and performance in sustainability and ethical practices. Let’s break down the components:
Environmental criteria consider how a company performs as a steward of nature. This includes how it handles issues related to climate change, waste management, water usage, and its overall impact on ecosystems. Companies report on their carbon footprint, energy efficiency, pollution, and resource conservation practices.
Social criteria examine how a company manages relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and the communities where it operates. This covers aspects like labor standards, diversity and inclusion, community engagement, human rights, and customer satisfaction. Companies often report on their efforts to create a positive social impact and ensure fair treatment and well-being of all stakeholders.
Governance involves a set of rules or principles defining rights, responsibilities, and expectations between different stakeholders in the governance of corporations. It includes issues such as board diversity and structure, executive pay, audits, internal controls, and shareholder rights. The aim is to ensure transparency, fairness, and accountability in a company’s dealings with its shareholders and the wider community.
ESG reporting is becoming increasingly important as investors and consumers show greater interest in sustainable and ethical business practices. It provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s commitment to achieving social and environmental objectives alongside financial performance. This reporting can help stakeholders assess the long-term value and risk profile of companies, guiding investment decisions and consumer preferences.
Why Does Your Company Need ESG Reporting?
Implementing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting can benefit a company in numerous ways, addressing both internal improvements and external perceptions.
Here's why your company might need ESG reporting:
Investor Attraction and Retention
Investors increasingly consider ESG factors as part of their analysis process to identify material risks and growth opportunities. ESG reporting can attract a broader investor base and retain investors who are focusing more on sustainability and responsible investing.
Regulatory Compliance
As governments and regulatory bodies worldwide heighten their focus on sustainable development and corporate responsibility, ESG reporting helps companies stay ahead of regulatory changes and ensure compliance. It positions a company as a forward-thinking and responsible entity.
Risk Management
ESG reporting allows companies to identify, assess, and manage environmental, social, and governance risks before they escalate. Understanding these risks can prevent costly incidents and enhance decision-making processes.
Brand Reputation and Trust
Companies that actively engage in ESG reporting can improve their brand image, build public trust, and strengthen stakeholder relationships. It demonstrates a commitment to ethical practices, sustainability, and social responsibility, which can enhance customer loyalty and employee satisfaction.
What Regulations Exist for ESG Reporting?
The landscape of regulations and standards for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting is evolving rapidly as governments, regulatory bodies, and industry groups recognize the importance of transparency in corporate sustainability and ethical practices. Here’s an overview of some key regulations and standards that exist for ESG reporting:
Global Initiatives and Standards
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
GRI is one of the most widely adopted global standards for sustainability reporting, offering a comprehensive framework for companies to report on their environmental, social, and governance impacts.
Sustainability Accounting Standard Board (SASB)
SASB provides industry-specific standards that help companies disclose material sustainability information to investors.
Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosure (TCFD)
TCFD offers recommendations for companies to disclose clear, comparable, and consistent information about the risks and opportunities presented by climate change.
CDP (formerly Carbon Disclosure Project)
CDP runs a global disclosure system that enables companies, cities, states, and regions to measure and manage their environmental impacts.
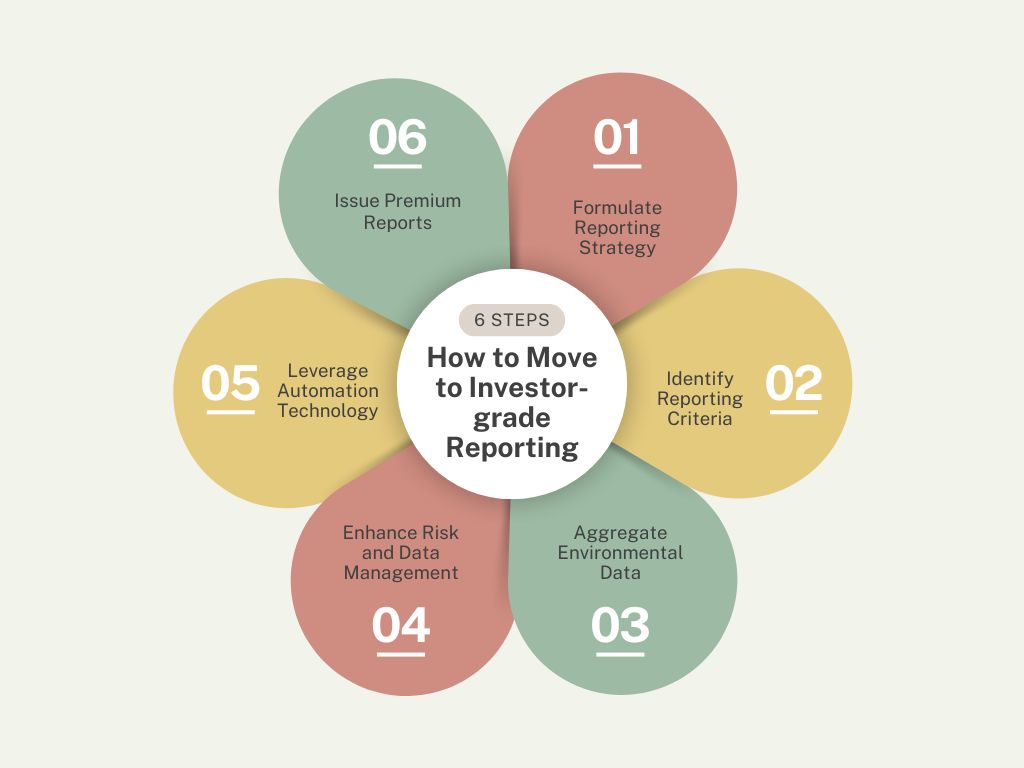
How to Move to Investor-grade Reporting
How We Support Your ESG Reporting
Materiality Assessment
We assist in identifying and prioritizing the ESG issues that are most significant to your stakeholders and business operations.
ESG Strategy Development
We help define your ESG goals and create a roadmap for achieving them, aligning with your business strategy.
Data Management and Analysis
We support the collection, validation, and analysis of ESG data, ensuring accuracy and completeness for reporting.
Reporting Frameworks Alignment
e guide you on aligning with relevant ESG reporting frameworks such as GRI, SASB, TCFD, and others applicable to your industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
Our Latest Findings on ESG Reporting
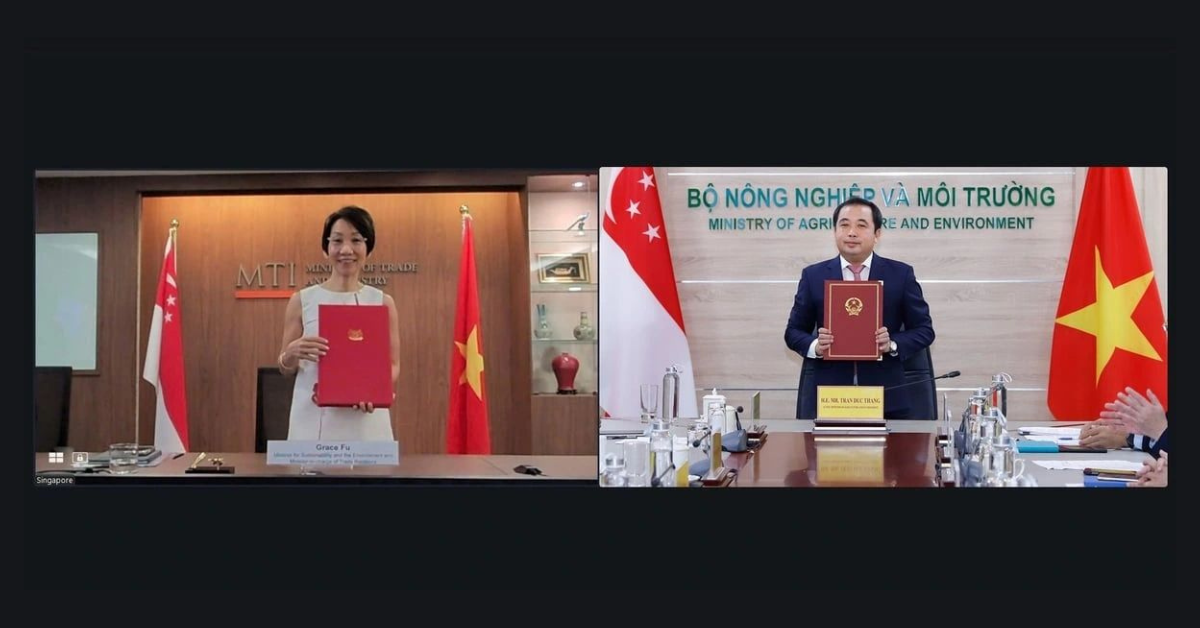
Source: LinkedIn (Grace Fu) 16 September 2025 — Singapore and
29 August 2025 – Malaysia’s Ministry of Energy Transition and
On 19 August 2025, Singapore and Thailand signed a bilateral